As we all know that the Google does not have unlimited time or resources to crawl every website in full.
Instead of reading an entire page word by word, Google follows a smarter process.
First, it discovers your URL.
Then, before deeply processing the content, it looks at the head section of the page to quickly understand what the page is about.
This is exactly why the <head> section has always been critical for SEO.
We add:
- Meta title
- Meta description

These elements help define the intent of the page at a high level.
But here’s the problem.
In today’s search environment, meta tags alone are no longer enough to clearly explain context, relationships, and meaning especially for AI-driven systems.
So what happens if the head section doesn’t provide enough structured information about the page?
Google has to guess.
And whenever Google has to guess, accuracy drops.
This is where schema markup comes in.
Schema markup adds structured, contextual information inside the head section that explains:
- What this page represents
- What entity it belongs to
- How it connects to the rest of the website
Instead of forcing search engines to interpret meaning from raw text, schema markup tells them directly.
In simple terms:
Meta tags describe intent.
Schema markup describes meaning.
And that difference is what allows Google and AI systems to understand your website faster, clearer, and more accurately.
What Is Schema Markup in SEO?
Schema markup (also known as structured data) is a special layer of code that helps search engines understand the meaning of your content, not just read the words on the page.
When Google crawls a webpage, it can see text, images, and links but without schema, it still has to interpret what those elements represent.
Schema removes that ambiguity.
It explicitly tells search engines:
- What this page is about
- What type of content it contains
- What real-world entity it represents
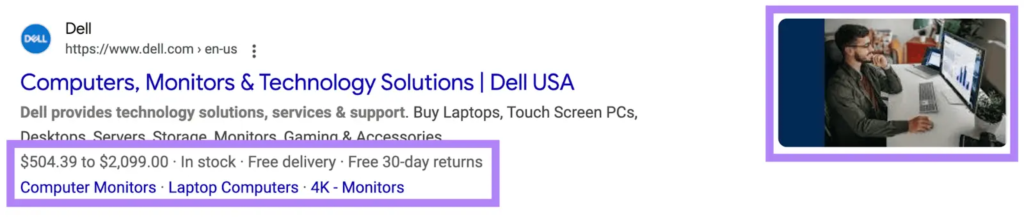
Because of this clarity, schema markup makes your pages eligible for enhanced search results, commonly known as rich snippets.
Let’s understand this by a real life example
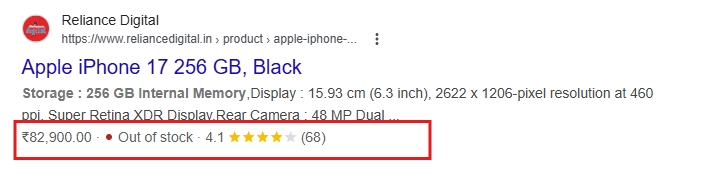
Let’s say you run an ecommerce website selling smartphones.
Without schema markup, Google can only see:
- Product name in text
- Price written somewhere on the page
- Stock status hidden inside content
Google has to interpret all of this on its own.
But when you add Product schema, you clearly tell Google:
- This page is a Product
- This is the price
- This item is in stock
- These are the ratings and reviews
Because of this structured clarity,
Google may display extra details directly in search results such as price, availability, and review stars which makes the listing far more informative for users.
Why Is Schema Markup Important for SEO?
Search engines don’t think like humans.
When a person visits your website, they immediately understand:
- What your business does
- What a page is about
- Whether they can trust the information
But for Google and now AI systems this understanding is not automatic.
They rely on signals, structure, and context.
That’s where schema markup becomes important.
How Schema Helps Google Understand Your Website Easily
Without schema, Google has to infer meaning from raw content.
For example:
- Is this page a service or just an informational article?
- Is this number a price, a phone number, or a random statistic?
- Is this brand the author, the publisher, or just mentioned in the content?
Schema markup removes this confusion.
It clearly tells Google:
- What type of page this is
- What entity owns it
- What the main topic or service is
- How different elements are related
Instead of guessing, Google gets clear instructions.
Think of schema as structured context, not extra code.
Why Schema is Also Important for AI Search Like (ChatGPT, Grok, and Gemini)
Search is no longer limited to “10 blue links.”
Today, people get answers from:
- ChatGPT
- Google AI Overviews
- Gemini
- Grok
- Other AI-powered search systems
These systems don’t just crawl pages they select sources they trust and understand.
AI prefers content that is:
- Well-structured
- Clearly attributed
- Easy to interpret
- Entity-based
Schema markup helps your website meet all of these conditions.
It makes your content machine-readable, which increases the chance that AI systems:
- Understand what your page represents
- Attribute information correctly
- Use your content in AI-generated answers
In short:
Schema helps your website speak the language of AI.
What Happens If You Don’t Use Schema?
When schema is missing:
- Google relies only on text interpretation
- Context can be misunderstood
- Your pages may be skipped for rich results
- AI systems may prefer better-structured competitors
You don’t get penalized but you lose visibility opportunities.
And in modern SEO, losing visibility is often worse than losing rankings.
Let’s understand this with a simple real life example
Imagine you walk into a large library.
Some books have:
- Clear titles
- Categories
- Author names
- Summary labels
Other books are placed randomly with no labels.
Which books would be easier to:
- Understand?
- Recommend?
- Use as a reference?
Search engines and AI work the same way.
Your website content is the book.
Schema markup is the label, category, and index card that explains what the book is about.
Without it, machines have to guess.
With it, everything becomes clear.
Common Types of Schema Markup and How to Use Them
Not every page on your website needs the same schema.
Each schema type has a specific purpose, and using the right one on the right page helps search engines and AI systems understand your site faster and more accurately.
Let’s go through the most common and important schema types in simple language.
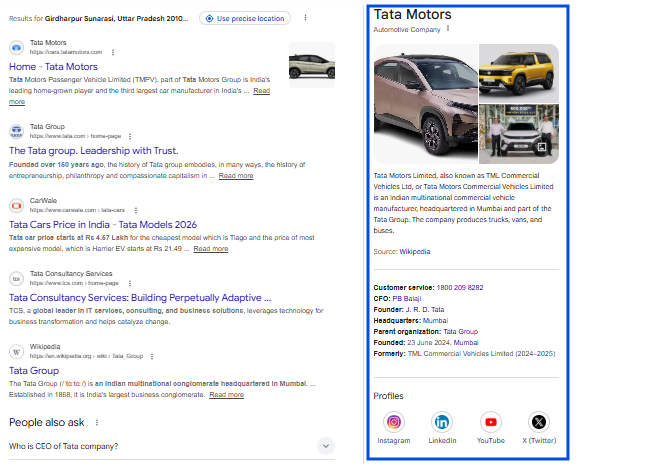
1. Organization Schema
Organization schema markup tells search engines more about your business, such as its name, logo, address, contact details, and social profiles.
It helps Google clearly identify your brand and can support visibility in knowledge panels and brand-related search results.
On Which Pages Organization Schema Should Be Use
Use it on:
- Homepage
- Site-wide (recommended)
This is your identity schema. It tells Google and AI systems that all pages belong to the same brand.
2. Website Schema
Website schema markup explains that a page belongs to an official website and how that website is structured.
It helps Google understand your site as a single entity and may enable features like the sitelinks search box in branded searches.
On Which Pages Website Schema Should Be Use
Use it on:
- Homepage
- Site-wide
3. WebPage Schema
WebPage schema markup describes the purpose of a specific page on your website.
It helps search engines understand whether the page is a homepage, contact page, about page, or another type of core page.
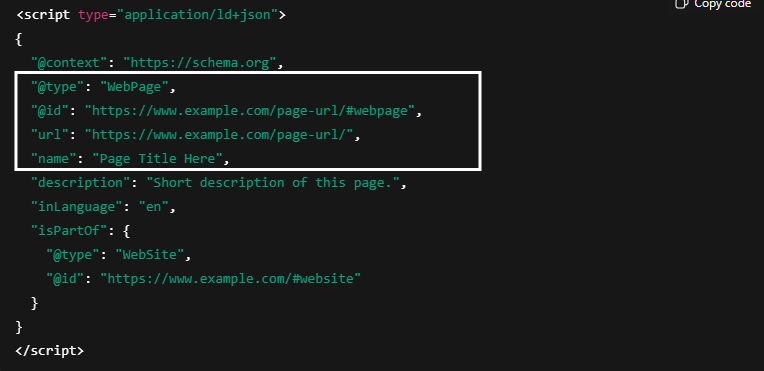
On Which Pages WebPage Schema Should Be Use
Use it on:
- Homepage
- Important static pages
It acts as the base layer for page-level understanding.
4. Article / BlogPosting Schema
Article (or BlogPosting) schema markup tells search engines that your content is an article or blog post,
along with details like author, publish date, and topic.
It helps Google and AI systems correctly classify and attribute your content in search results.
On Which Pages Article Schema Should Be Use
Use it on:
- Blog posts
- Guides
- Educational content
Improves eligibility for article enhancements and helps AI systems correctly attribute content.
5. Service Schema
Service schema markup explains what service you offer and who provides it.
It helps search engines clearly distinguish service pages from informational content, improving relevance for service-related searches.
On Which Pages Article Schema Should Be Use
Use it on:
- Agency or consultant websites
- Service pages
It clearly separates service pages from blog content, reducing confusion.
6. Product Schema
Product schema markup provides structured details about a product, such as price, availability, ratings, and offers.
It makes product pages eligible for rich results, which can display price and stock information directly in search results.
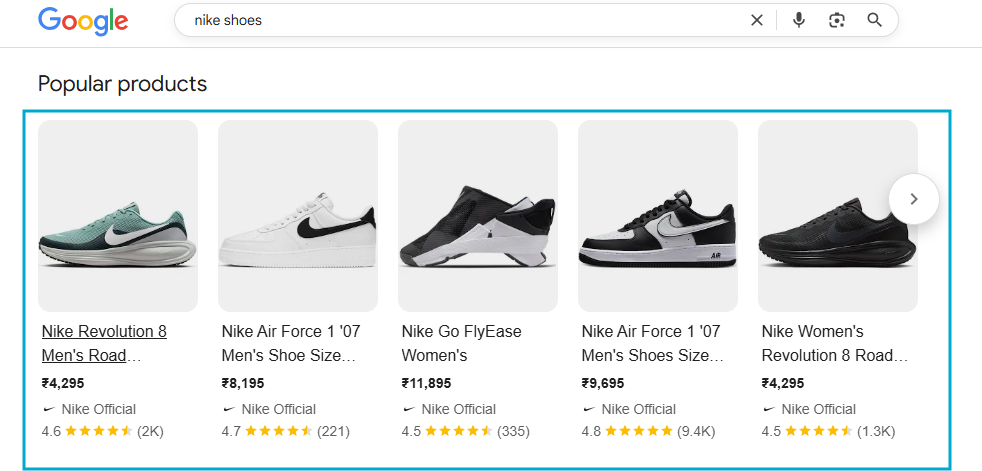
On Which Pages Product Schema Should Be Use
Use it on:
- Ecommerce product pages
7. FAQPage Schema
FAQPage schema markup tells search engines that a page contains frequently asked questions and answers.
When used correctly (with visible FAQs), it can expand your search result and show questions directly in Google.
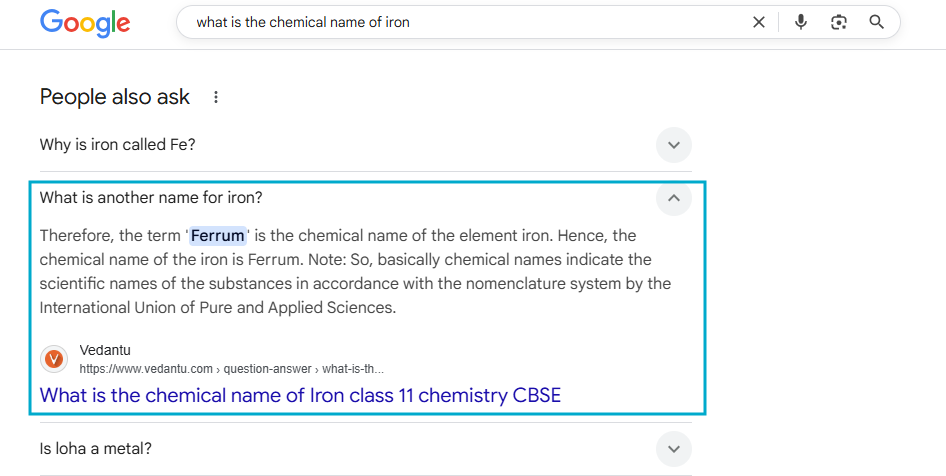
On Which Pages FAQ Schema Should Be Use
Use it on:
- Pages with visible FAQs only
8. Review / AggregateRating Schema
Review schema markup highlights customer ratings and reviews for a product or service.
It helps build trust and can display star ratings in search results when Google allows it.
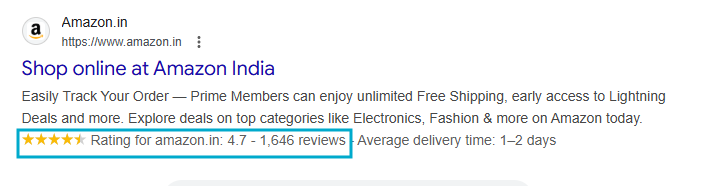
On Which Pages Review / Aggregate Rating Schema Should Be Use
Use it on:
- Product pages
- Service pages (with real reviews)
9. Breadcrumb Schema
Breadcrumb schema markup shows the hierarchical structure of your website pages.
It helps Google understand page relationships and improves navigation clarity in search results.
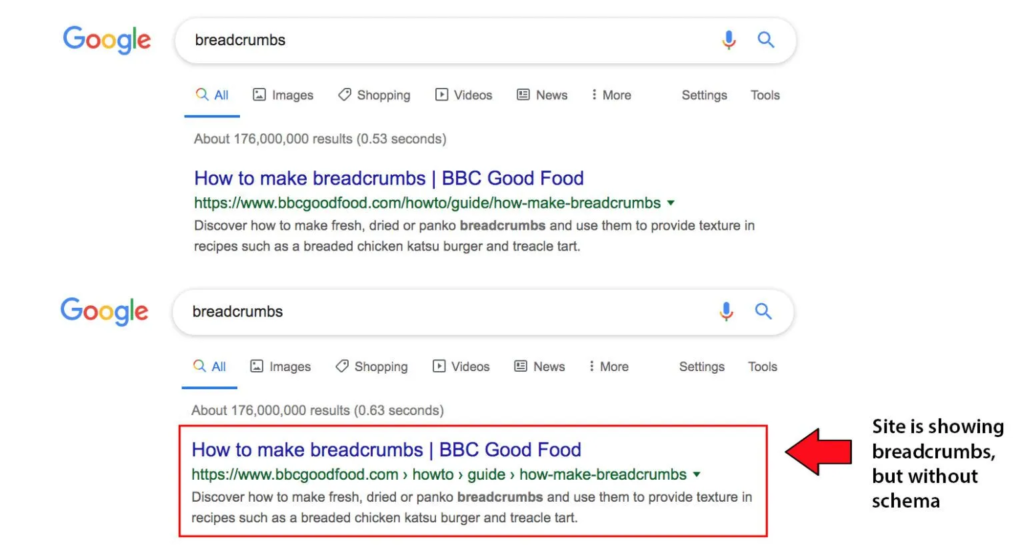
On Which Pages Breadcrumb Schema Should Be Use
Use it on:
- Blogs
- Categories
- Ecommerce sites
Schema Markup Formats (How Schema Is Written)
Schema markup uses a shared vocabulary from Schema.org to help search engines clearly interpret what your content means and how it should be presented in search results.
This structured information is added on top of HTML, which is the foundational markup language that structures every webpage. While HTML tells browsers how to display a page, schema markup tells search engines how to understand it.
To implement schema markup, Google supports three main formats. Each format communicates the same information the difference lies in how the data is written and embedded into a webpage.
These formats allow search engines to read structured context without guessing, making your content easier to process, classify, and display in enhanced search results.
1. JSON-LD (Recommended)
JSON-LD is the most widely used and Google-recommended format.
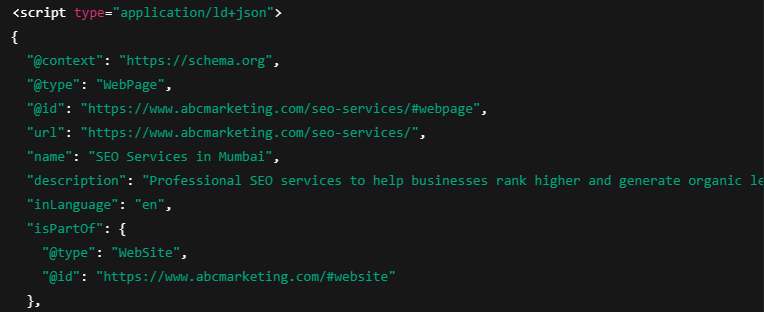
Why it’s preferred:
- Easy to read and maintain
- Doesn’t interfere with website design
- Can be added entirely inside the
<head>section - Works perfectly for large and dynamic websites
This is the format used by most modern websites and SEO professionals.
If you are starting today, JSON-LD should always be your first choice.
2. Microdata
Microdata adds schema directly inside HTML elements.
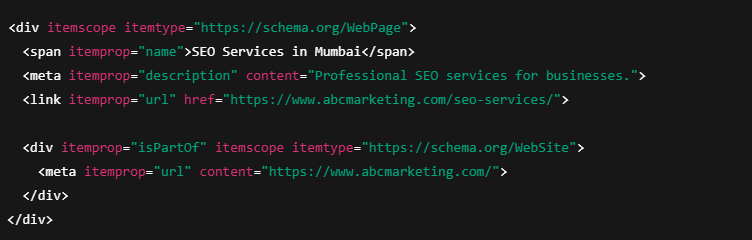
That means schema is mixed with:
- Page content
- HTML tags
Limitations:
- Harder to manage
- Increases risk of errors
- Difficult to scale across large sites
Microdata was popular in the early days of schema but is rarely recommended today.
3. RDFa
RDFa is another HTML-based format similar to microdata.
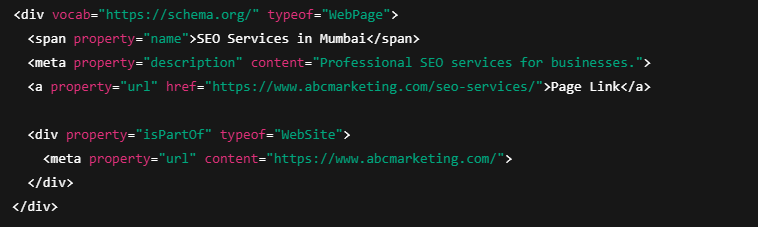
It is mostly used in:
- Academic projects
- Data-heavy or semantic web applications
For SEO and marketing websites, RDFa offers no practical advantage over JSON-LD.
Which Schema Format Should You Use?
| Format | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| JSON-LD | ✅ Best choice |
| Microdata | ⚠️ Avoid if possible |
| RDFa | ❌ Not needed for SEO |
